
Guided by a growing consensus among nutrition experts, Canada’s Food Guide1, The Planetary Health Diet – EAT2, and a growing number of health and environmental associations,3 call for an increased consumption of fruits and vegetables. Simultaneously, they are advocating for reductions in the consumption of meat, dairy and eggs – calling for swaps with plant proteins4, or lower fat versions. Health Canada recommends that Canadians “choose proteins that come from plants everyday.”5

In the review article, Plant-Based Dietary Patterns for Human and Planetary Health6 the authors write, “It is time for developed nations to commit to red meat reduction targets and shift to plant-based dietary patterns.” They recognize that significant barriers exist and call on governments to help overcome those barriers.7
A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010 estimated that increased consumption of whole grains, vegetables, nuts and seeds, and fruit could prevent millions of premature deaths each year.7 Both the Dieticians of Canada and the American Association of Dieticians have stated that well planned plant-based diets have substantial health benefits and are appropriate for all stages of human development.8,9
The information in this graphic was taken from the Global Burden of Disease study7


Cardiovascular Health
Canada’s Food Guide: Resources for health professionals and policymakers10, describes cardiovascular disease as a serious public health concern in Canada. Almost 50% of deaths from cardiovascular disease were attributed to dietary risks in 201710. Dietary risks include low intake of nutritious foods, such as fruit and vegetables. In Canada, fruit and vegetable intakes are consistently low despite recommendations for Canadians to consume more10.
A paired study of identical twins recently conducted by researchers at Stanford University11 Found that a vegan diet improves overall cardiovascular health significantly more than does a healthy omnivorous diet. “In this randomized clinical trial of the cardiometabolic effects of omnivorous vs vegan diets in identical twins, the healthy vegan diet led to improved cardiometabolic outcomes compared with a healthy omnivorous diet”12.

Diabetes Prevention and Management
A diet containing more plant fibre, such as whole grains, has been shown to lower the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes13 and to be good in managing the disease.14 Whole and minimally processed plant foods are high in fibre, low in saturated fats, and have been found to reduce insulin resistance and improve glycemic control.15, 16 A recent systematic review found that a vegan diet is associated with reduced incidence of diabetes.17 The American Diabetes Association has named beans a “super food,” and state that beans and legumes provide high quality protein, health fats and fiber.18


Cancer Risk Reduction
The Adventist Health Study-2, a long-term population health study, found that people who consumed a plant-rich diet experienced a reduction of the overall incidence of several cancers19. Plant-rich diets have been found specifically to reduce the risk of colorectal cancer, as well as overall cancer mortality.20
In a review comparing ketogenic diets to plant-based diets, it was found that “the collective evidence supports plant-enriched diets vs ketogenic diets for the reduction of cancer risk and the improvement of metabolic disorders in survivors.” The authors emphasize there’s no rigorously tested diet to recommend for treatment of cancer in any post-diagnostic setting, but available data supports plant-based diets when compared to ketogenic diets for prevention.21

Weight Management
Globally, we are experiencing an unprecedented level of diseases related to overconsumption and under-nourishment. According to the EAT-Lancet Commission,22 worldwide, 2.1 billion adults are overweight or obese. Obesity, and simply being overweight are associated with increased risk for a range of chronic diseases7.
Plant foods are generally low in calories and saturated fats, but high in fibre and antioxidants. Including unprocessed plant foods in your diet can lead to healthy weight loss23. Well designed vegan diets have been found to be among the most effective for weight loss, and all the better for healthy weight loss.24, 25

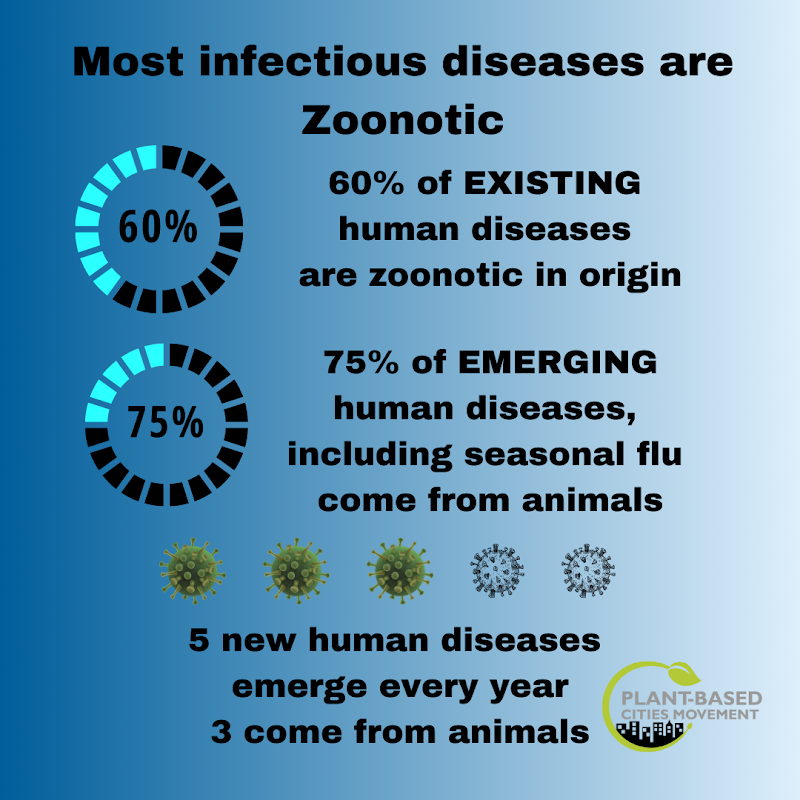
Zoonotic diseases
The majority of infectious diseases in humans originate from animals. Many experts are warning that as agriculture continues to intensify, modern industrial farming has created serious risks of new and emerging infectious diseases.26, 27 Confinement, genetic homogenization, concentrated animal waste, and movement of farm workers between farms are all aspects of industrialized farming that are putting us all at risk for disease development and transmission.
This figure was created based on information obtained from the National Public Health Institute publication “One Health, Many Approaches: CDC Fosters a One Health Strategy in NPHI”28
Avian Influenza
Experts are specifically concerned about H5N1, a strain of avian influenza that has a very high mortality rate when contracted by humans29. Cases of H5N1 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) have been reported by the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) in both commercial poultry and backyard flocks in most provinces since 2021.30 According to the Chicken Farmers of Canada the current avian influenza trend is persistent and is the largest outbreak ever seen in Canada.31 Over 7.5 million commercial poultry and egg-producing birds have been culled across Canada as of July 2023.32 Human infections are rare, but serious, and most common among people working directly with infected poultry.33 While HPAI risk remains low and has not been detected in mammal-to-person or person-to-person transmission in Canada (as of July 2023),34 the greater the extent of bird and other animal infection by this disease, the greater is the risk that a form readily transmitted among humans may develop.35 At any one time globally, nearly 80 billion farmed animals are being raised to provide food for human consumption. Over 70 billion of these farmed animals are chickens.36
Further resources to assist with plant-based meal planning can be found at the following links:
Brenda Davis: My Vegan Plate and Designing an Optimal Diet.
Try plant-based for 21 days here.
Dr. Pamela Fergusson, a Canadian plant-based dietician and health expert recommends a whole foods plant-based diet.
Plant-Based Health Professionals of the UK have several excellent fact sheets free to download.
Notable Nutrients are explained in this fact sheet:37
Fiber
Abundant in a whole food plant based diet, promoting a healthy gut microbe, improving satiety, ↓cholesterol, ↓ cancer.
Vitamin B12
Not made by plants or animals but microorganisms. Deficiency is an issue for all dietary patterns. Supplementation is required on a whole food plant based diet (tablet or fortified foods).
Calcium and Vitamin D
Calcium is easily obtained from plant sources, including greens, beans, and fortified foods. No negative effect on bone health if dairy is avoided. Vitamin D is mainly made by the action of the sun on skin. A supplement is recommended for all during the winter months.
Omega 3 Fatty Acids
Plant sources include algae, walnuts, flax seeds, hemp seeds, chia seeds, and soya beans. This avoids the pollutants in fish such as mercury, dioxins, PCBs.
Iron
Iron stores may be lower but will not be associated with deficiency. The avoidance of haem iron is beneficial given its role in cancer, diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Iodine, zinc and selenium
Iodized salt and seaweed provide iodine, which is needed in moderation. Phytates in grains and beans can reduce zinc absorption, however, soaking, fermenting and sprouting can increase absorption. Good sources of zinc are tempeh and miso, nuts and seeds. Selenium is found in grains, seeds, and nuts. Just two Brazil nuts will provide your daily requirement.
References